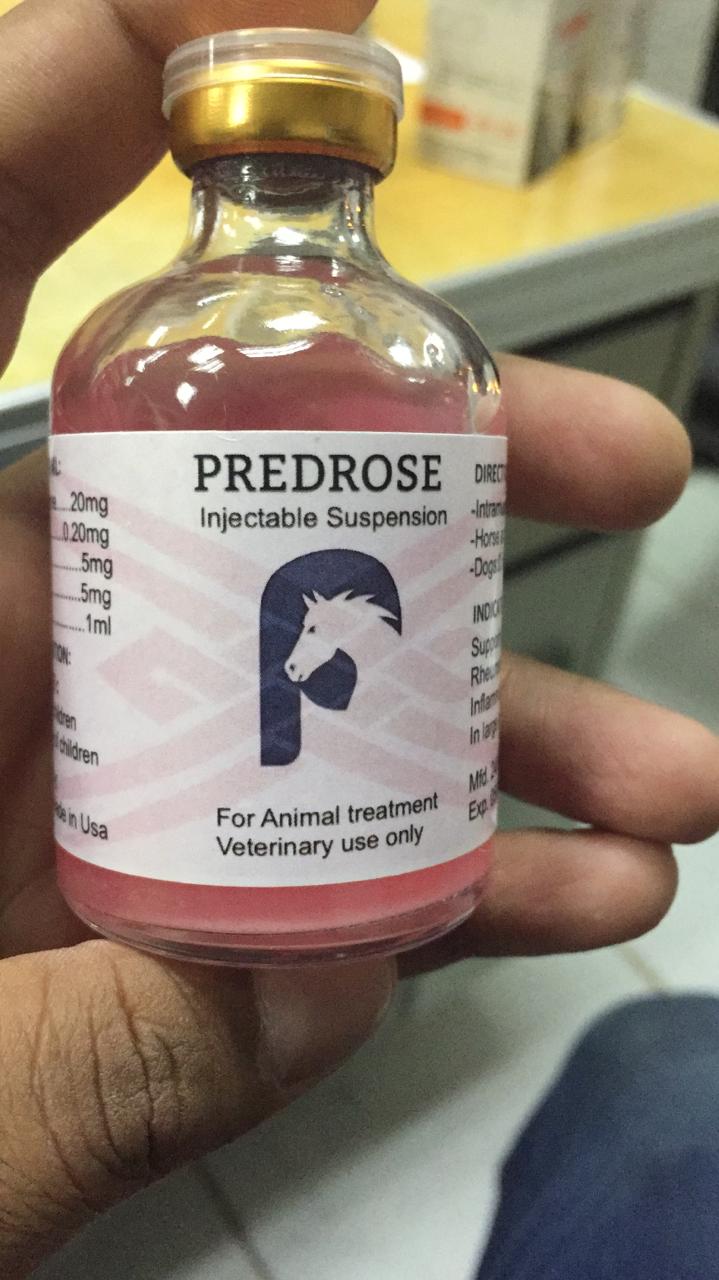
predrose injectable The combination of phenylbutazone and dexamethasone enhance animal’s resistance during training and race Optimal product for racing animals Anti-inflammation, analgesic, antipyretic
METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Apply 5 ml for 5 days – IM (suspend 7 days before the race).
IV and IM administration
– Horse and camel: 4 ml/100 kg BW
– Dogs: 0.5 ml/10 kgs BW
Withdrawal time: 07 days before slaughter
Contra-indication: Do not use for hypersensitive animals to any components
PRESERVATION: Store in a cool place and keep out of direct sunlight.
The FLUMAX product must be administered by intramuscular or intravenous routes, every 24 hours with intervals of 3 to 5 days at the discretion of the Veterinarian, using a sterile and disposable syringe and needle. Aseptic procedures must be used in the application.
In horses, administer 1 ml of the product for every 45 kg of live weight, which corresponds to 1.1 mg of Flunixin Meglumine, to relieve pain associated with colic/endotoxemia. predrose injectable
Precautions and Warnings:
Doses greater than 10 ml of the product should be divided into two or more application points.
Respect the indications for dose and duration of treatment.
Do not apply intra-arterially.
Obey the product’s storage instructions.
Use sterile syringes and needles, observing good asepsis practices.
Apply with caution to animals with gastrointestinal ulceration or pre-existing renal, hepatic or hematological disorders.
It is recommended to avoid or apply the drug to pregnant females with maximum precaution and supervision by the Veterinarian.
If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue administration of the product immediately.
Do not store the product near food, beverages, other medications, personal or household hygiene products.
Avoid smoking or eating while handling.
Do not wash empty containers or throw them into rivers or springs. Do not reuse empty packaging, which must be destroyed by inciretion.
Wash hands after handling.predrose injectable
The drug must be used under the guidance of a Veterinarian. The main toxicities of NSAIDs are associated with the gastrointestinal, hematopoietic and renal systems.
Gastrointestinal damage is the most common and serious side effect. Gastroduodenal erosion and ulceration reflect prostaglandin E2-mediated inhibition of bicarbonate and mucus secretion, epithelialization, and mucosal blood flow.
All NSAIDs are capable of impairing platelet activity related to thromboxane synthesis.
Analgesic nephropathy is a common adverse effect of NSAIDs in humans, however, it does not occur as often in domestic animals, in part because the drugs are not used as chronically. In the kidney, vasodilating prostaglandins are protective, ensuring arterial and renal vasoconstriction. The loss of this protective effect becomes important in patients with impaired renal function. Patients predisp




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.